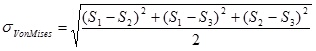The internal forces and moments exist at every point on the middle surface of the shell element. They represent the resultants of different normal and shear stresses over the element thickness. The internal forces have the units of force per unit length and the internal moments have the units of moment per unit length.
The in-plane or membrane results include the normal forces Fxx, Fyy and shear force Fxy. The out-of-plane results include the shear forces Vx, Vy and bending moments Mxx, Myy, Mxy. Mxy is also called twisting moments. It is important to differentiate these forces and moments
The following figure shows the positive direction of the internal forces and moments of a shell. They represent forces and moments at one point on the middle surface of the element. The program outputs these forces and moments at the four corner nodes and /or at the center of the element. You may use Analysis Results > Results Diagrams > Contour Diagram to see the distribution of these and other resultants. Generally speaking, internal forces or moments (or result in general) are different across element boundaries. You have the option to average forces and moments for adjacent elements at nodes. To do that, click Analysis > Analysis Options.
the in-plane axial and shear forces |
|
|---|---|
the out-of-plane bending shears |
the out-of-plane bending moments |
Based on the internal forces and moments, the program computes the internal stresses at the shell bottom (the –z side) and top (the +z side) as follows. The stresses are expressed in the local coordinate systems. The stress directions correspond to the in-plane normal axial forces and shear, and the out-of-plane shears.
![]() (@ bottom) or
(@ bottom) or ![]() (@ top)
(@ top)
![]() (@bottom) or
(@bottom) or ![]() (@ top)
(@ top)
![]() (@bottom) or
(@bottom) or ![]() (@ top)
(@ top)
![]()
![]()
The program also outputs in-plane principal forces and angles, and out-of-plane principal forces, moments, and angles. In addition, principal stresses S1, S2, and S3 are computed based on the stresses ![]() as follows:
as follows:
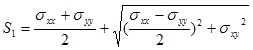
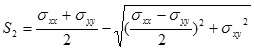
![]()
The Von Mises stress, which is often used to estimate the yield of ductile materials, is then computed as follows: