The three methods of inputting active soil pressure are the Equivalent Fluid Pressure (EFP) method, Rankine method and Coulomb method.
With the Equivalent Fluid Pressure (EFP) method, the soil active pressure is defined by an equivalent fluid pressure in psf per foot of depth (e.g. 35 psf).
With the Rankine or Coulomb method, you can input the angle of internal friction and the program will compute the horizontal (and vertical, if applicable) Ka by the respective formulas.
For a level backfill, both the Rankine and Coulomb formulas give the same result, except that the latter also takes into account frictional resistance of the wall surface, and inclination of the wall surface (i.e. batter).
The Rankine Formula
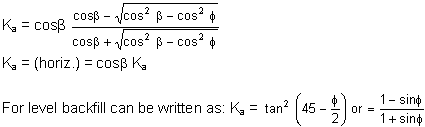
The Coulomb Formula
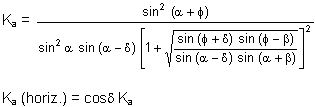
For both formulas:
β = Angle of backfill slope
ϕ = Angle of internal friction
α = 90° - wall slope angle from horizontal
δ = Angle of friction between soil and wall (Assumed in program to be ϕ/2 when heel does not project beyond the soil face of the wall. Otherwise, the failure plane is assumed to occur at the end of the heel projection (soil-on-soil), and δ is assumed to be ϕ.)