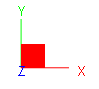
The global coordinate system is a fixed Cartesian system that is used for entire model. The three axes are denoted by capital letters X, Y and Z. They follow the right-hand rule. By default, that is, when a model is not rotated for viewing purpose, the X axis points from left to right (horizontal), the Y axis points from bottom to top (vertical), and the Z axis points from screen to out of screen (perpendicular to screen).
The global coordinate system is used in the following input:
-nodal coordinates, nodal loads
-degrees of freedom related to nodes, supports and springs
-self weights
-point, line, and surface loads on members and finite elements [may also be specified in the element local coordinate system]
The global coordinate system is used in the following output:
-nodal displacements
-support and spring reactions
-brick stresses